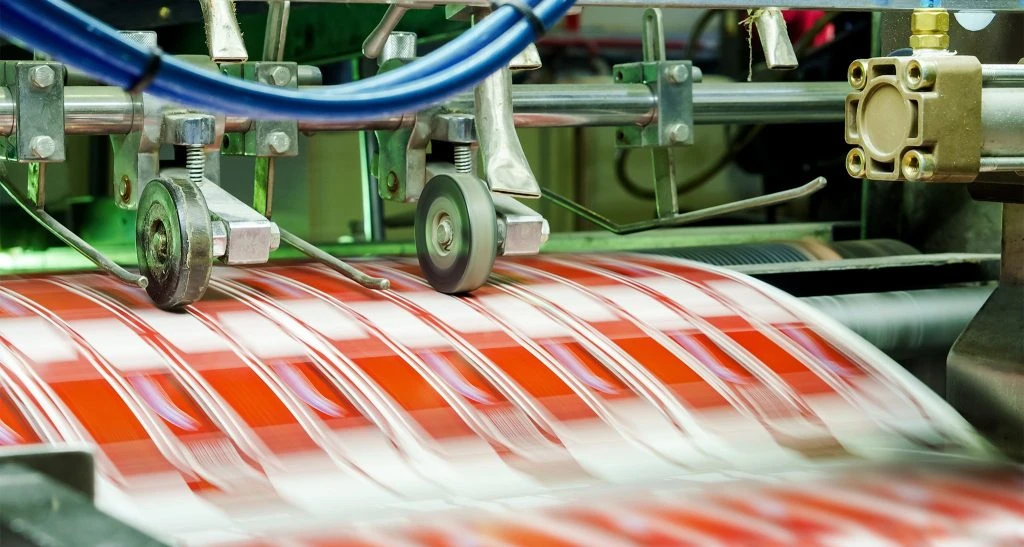
Introduction
The varnishing process involves applying a layer of colorless transparent coating on the surface of printed materials, which, after leveling and drying, forms a thin and uniform transparent glossy layer on the surface of the printed materials. This process effectively enhances the glossiness, smoothness, water resistance, light resistance, and wear resistance of the products, serving to protect and beautify them while enhancing their practical value.
Working Principle
The principle of varnishing in printing mainly involves applying (or spraying, printing) a layer of colorless transparent coating on the surface of printed materials. After processes like leveling, drying, pressing, and curing, this layer of coating forms a thin and even transparent glossy layer on the surface of the printed materials. The principles include:
Selection of coating: Choose appropriate varnish based on the material, color, and desired glossiness of the printed materials. Common varnishes include oil-based, water-based, and UV-curable types.
Coating application: Use coating machines or other coating equipment to evenly apply the varnish on the surface of the printed materials. Control the thickness and uniformity of the coating during application to ensure the final glossy layer has a good appearance and performance.
Leveling: After the coating is applied to the surface of the printed materials, it needs some time for leveling. During leveling, the coating will automatically spread and flow on the surface of the printed materials to eliminate unevenness and traces.
Drying: After leveling, the coating needs to be dried. During drying, the solvent in the coating evaporates, causing the coating to gradually cure into a film. The drying temperature and time need to be adjusted according to the type of coating and the material of the printed materials.
Pressing: After the coating is dried, a pressing machine can be used to press the printed materials to enhance the smoothness and glossiness of the coating layer, and to increase the wear resistance and light resistance of the printed materials.
Forms of Varnishing
Coating Varnishing (Regular Varnishing)
Apply varnish oil directly onto the printed materials and dry it.
Features: Simple process, low cost, good varnishing effect.
Press Varnishing
After coating varnishing, use a pressing machine to roll and increase the surface glossiness.
Features: Relatively simple process, low cost, good varnishing effect.
UV Varnishing
Apply UV varnish oil on the surface of the printed materials, and cure it by UV irradiation.
Features: Non-volatile, energy-saving, glossy and sturdy film, corrosion-resistant, fast varnishing speed (up to 500m/min), suitable for online varnishing.
Composition and Classification of Varnishing Machines
Classification of Varnishing Machines
Water-based Varnishing Machine
Water-based varnishing: It uses water-based varnish for varnishing, which has characteristics such as high solid content, low viscosity, and non-toxicity. It also has good leveling and glossiness and can be diluted with water.
Wide applicability: Water-based varnishing machines are very suitable for the printing and processing of packaging materials in industries such as food and pharmaceuticals.
Good heat sealing: Water-based varnish has excellent heat sealing properties, and even when using cellosolve, it can achieve good heat sealing effects.
Strong wear resistance: Products processed with water-based varnish have good flatness and strong anti-curling ability, making them particularly suitable for packaging printed materials that require strong wear resistance. Especially in high-speed operation, such as cigarette labels, which need to withstand a lot of mechanical load, water-based varnish can meet the requirements of high transparency and wear resistance.
UV Varnishing Machine
High surface glossiness: UV varnishing machines can improve the surface glossiness of printed materials, making them have a more vivid and beautiful appearance.
Strong wear resistance: The surface of printed materials treated with UV varnishing machines forms a hard and wear-resistant transparent film layer, effectively enhancing the wear resistance of printed materials and making them more durable.
Fast curing speed: UV varnishing machines have a fast curing speed and can complete the varnishing process in a very short time, improving production efficiency.
Varnishing
Materials
Water-based Varnish
Water-based varnish refers to a liquid used to increase the glossiness, water resistance, and abrasion resistance of paper-printed products, applied either inline with a printing press or offline with a varnishing machine, with water as the carrier.
UV Varnish
UV varnish, also known as UV clear coat, is a transparent coating. After application on printed materials, it undergoes a transition from liquid to solid state through UV light exposure, providing durability against scratches and abrasions while presenting a glossy appearance. UV varnish mainly consists of UV curing resin, active diluents, photoinitiators, and other additives.
Varnishing Process and Procedure
Preparation
Firstly, identify the printed materials that require varnishing, typically selecting areas that need to highlight colors and patterns for varnishing treatment. Clean the printed materials to ensure the surface is free from dust, preventing any interference with the varnishing effect.
Selection of Varnishing Method:
Based on the requirements and characteristics of the printed materials, select an appropriate varnishing method. Common varnishing methods include UV varnishing, water-based varnishing, and solvent-based varnishing.
Preparation of Varnish
Choose the suitable varnish according to the selected varnishing method. Prepare or dilute the varnish as required, ensuring that the concentration and viscosity of the varnish are suitable for the varnishing needs of the printed materials.
Varnishing Process
Apply the varnish evenly onto the surface of the printed materials using professional varnishing equipment (such as UV varnishing machines or water-based varnishing machines). While varnishing can be done manually, mechanical equipment (such as varnishing machines) is typically used to ensure uniform application and efficiency.
Drying
After applying the varnish, drying is necessary. The drying method depends on the type of varnish and the characteristics of the printed materials. For water-based varnish, natural drying or hot air drying methods are commonly used. For UV varnish, rapid curing drying is achieved by using ultraviolet light irradiation.
Curing (Specific to UV Varnishing)
If UV varnishing is chosen, curing is required after drying. After UV varnish is applied to the substrate, it undergoes a curing process where the varnish flows and enters the UV radiation zone for curing. The curing process involves a chemical cross-linking process, where unsaturated carbon-carbon double bonds in the prepolymers and monomers (liquid) receive energy from the photoinitiator and cross-link polymerize into a network structure of molecules (solid).
Quality Inspection
Conduct quality inspection on the completed varnished and cured printed materials to ensure the varnishing effect meets requirements and there are no issues such as missed spots, unevenness, or incomplete curing.
Packaging
After varnishing is completed, package the printed materials to protect the varnished surface from scratching or contamination.
Advantages of Varnishing Process
Enhanced Print Quality
Increased Gloss: The surface gloss of varnished prints is higher, resulting in brighter colors and clearer images, thus enhancing the overall quality of the prints.
Improved Durability: Varnished prints exhibit enhanced surface durability, effectively resisting daily wear and tear, thereby extending the lifespan of the prints.
Waterproof and Stain Resistant: Varnished prints demonstrate certain waterproof and stain-resistant properties after varnishing treatment, better maintaining the cleanliness and aesthetics of the prints.
Highlighted Visual Effects
Spot Varnishing: Through spot varnishing treatment, key information or images in prints can be emphasized, making the visuals more three-dimensional and vivid, attracting the audience’s attention.
Gloss Contrast: The contrast in gloss between varnished and unvarnished areas enhances visual impact, making the prints more attractive.
Energy-efficient and Effective: The varnishing process is simple and efficient, enabling rapid curing and reducing energy consumption and emissions.
Improved Production Efficiency
Rapid Curing: Varnish has strong affinity and adhesion with ink, enabling rapid curing and shortening the production cycle.
Reduced Scrap Rate: Varnishing treatment stabilizes print quality, reducing scrap rates caused by quality issues.
Wide Application
Various Print Materials: The varnishing process is suitable for various print materials such as book covers, posters, brochures, packaging, etc., with broad application prospects.
Different Materials: This process can be applied to a variety of materials including paper, plastic films, expanding the range of material choices for prints.